Sepsis Awareness 3: The Facts

The DFW Hospital Council (DFWHC) Foundation has been coordinating the Sepsis Strike Force over the past five years. Led by Patti Taylor, the DFWHC Foundation’s director of quality and patient safety services, the group is made up of representatives from hospitals across North Texas inspired by the goal to create awareness on the dangers of sepsis in our community. Over the next six months leading to Sepsis Awareness Month in September, the Sepsis Strike Force will post blogs and informational graphics across social media to support their 2021 goal of raising community awareness.
Here are some critical facts about Sepsis:
• Sepsis is the leading cause of death in U.S. hospitals.
• Approximately 6% of all hospitalizations are due to sepsis and 35% of all deaths in-hospital are due to sepsis.
• Sepsis is the leading cause of readmissions to the hospital, with as many as 19% of people originally hospitalized with sepsis re-hospitalized within 30 days and about 40% re-hospitalized within 90 days.
• As many as 87% of sepsis cases originate in the community and not in the hospital.
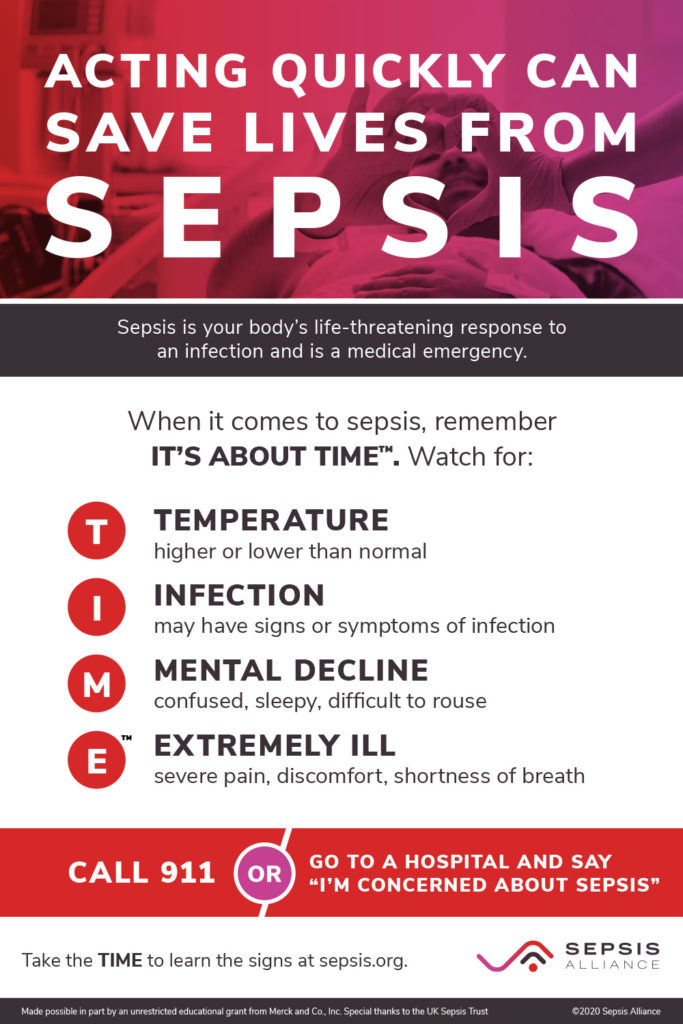
• The risk of mortality from sepsis increases by 4-9% for every hour treatment is delayed. As many as 80% of septic shock patients can be saved with rapid diagnosis and treatment.
• Sepsis is the most common complication observed in severe cases of COVID-19.9, 10 Recent research reports that hospitalized COVID-19 patients are 22% more likely to develop sepsis than hospitalized influenza patients, and four times as likely to develop severe septic shock.
Here is the human cost of Sepsis:
• Sepsis affects an estimated 49 million people worldwide each year, including more than 20 million children under age 5, and nearly 5 million older children and adolescents (ages 5-19).
• Sepsis takes 11 million lives around the world each year, contributing to 20% of all deaths globally and taking more lives than cancer. This is more than 20 deaths every minute.
• More than 1.7 million people in the U.S. are diagnosed with sepsis each year – one every 20 seconds – and the incidence is rising.
• 270,000 people die from sepsis every year in the U.S. – one every 2 minutes; more than from prostate cancer, breast cancer and opioid overdose combined.
• It is estimated that each year, more than 80,000 sepsis survivors are discharged to hospice after a sepsis hospitalization.
• Each year, more than 75,000 children in the U.S. develop severe sepsis and 6,800 of these children die, more than from pediatric cancers.
• Sepsis causes at least 261,000 maternal deaths every year worldwide and is driving increases in pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.
• Sepsis in the U.S. disproportionately affects the Black community; Blacks bear nearly twice the burden of sepsis deaths, relative to the Black population, as whites.
• In 2012, there were more than 13,700 sepsis-related amputations in the U.S. This works out to an average of 38 amputations per day.
Approximately 1% of sepsis survivors undergo one or more surgical amputations of a limb or digit as a result of sepsis.
• Sepsis survivors have a shortened life expectancy, are more likely to suffer from an impaired quality of life, and often experience worsened cognititve (mental) and physical function.
• Missed infections are the third most common cause of diagnostic errors identified in medical malpractice cases. Sepsis is the most common condition among missed infections in diagnostic errors.
Here is the economic cost of Sepsis:
• Sepsis is the #1 cost of hospitalization in the U.S. Costs for acute sepsis hospitalization and skilled nursing are estimated to be $62 billion annually. This is only a portion of all sepsis-related costs, since there are substantial additional costs after discharge for many.
• The average cost per hospital stay for sepsis is double the average cost per stay across all other conditions.
• Sepsis is the #1 cause of readmission to the hospital, costing more than $3.5 billion each year.